Description
At Gogain Industry Sdn Bhd, we offer the most comprehensive inventory of silver brazing alloys in the industry. Whatever your metal joining requirements, we have the materials ad technical abiloty to meet your needs. In close partnership with you, we develop solutions for the joining of metallic materials, tungsten carbide and ceramics. Not only do we recommend suitable brazing alloys, brazing pastes and fluxes for your special applications, but we also offer you our expertize on the brazing-orientated designs of your work pieces, how to optimize your brazing process, and on choosing suitable brazing machines and furnaces.
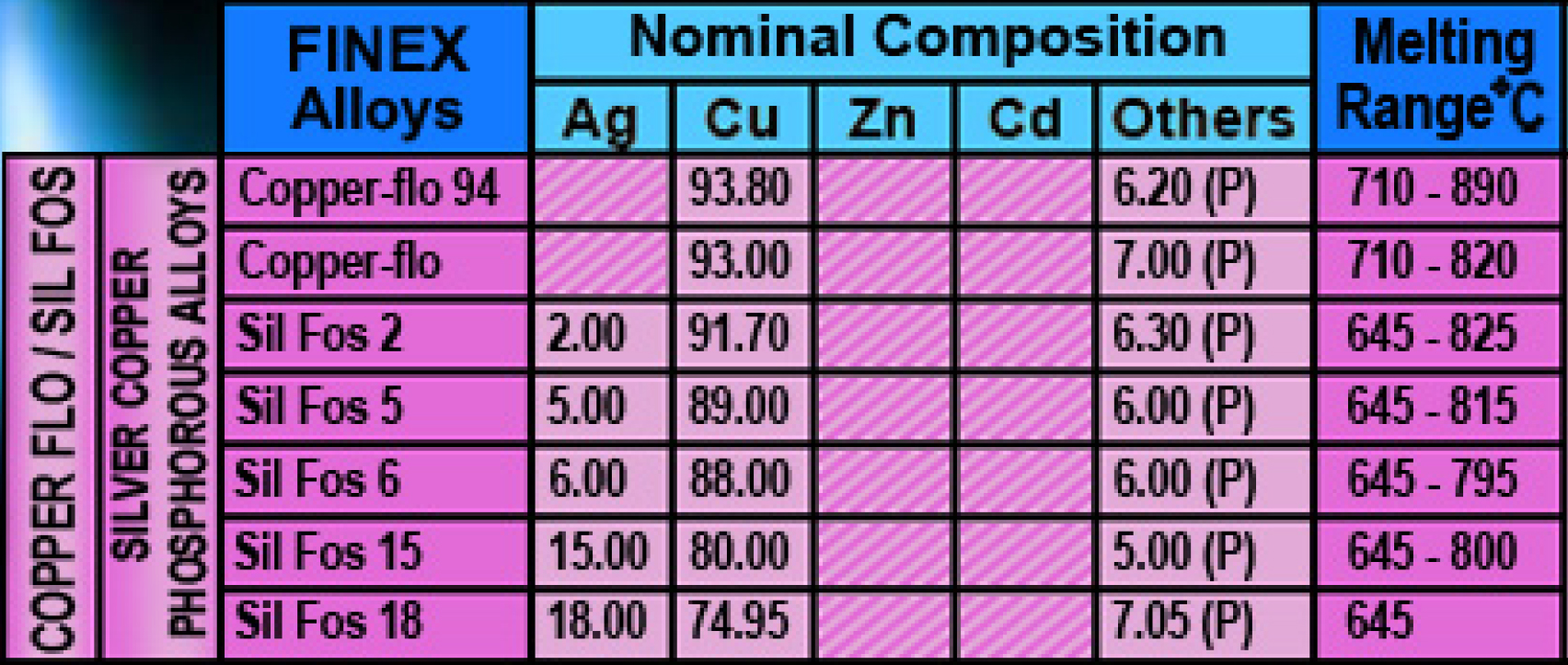
Remarks
Service Temperature :
The brazing alloys can be used for service temperature between -55C up to +150C.
Parent Metals :
The phosporous-containing brazing alloys on this page have been developed specially for joining copper-to-copper or copper-based materials to one another, Due to their phosphorous content, it is possible to eliminate the use of a flux when brazing copper-to-copper. The brazing alloys must not be used if the service environment contains sulphur.
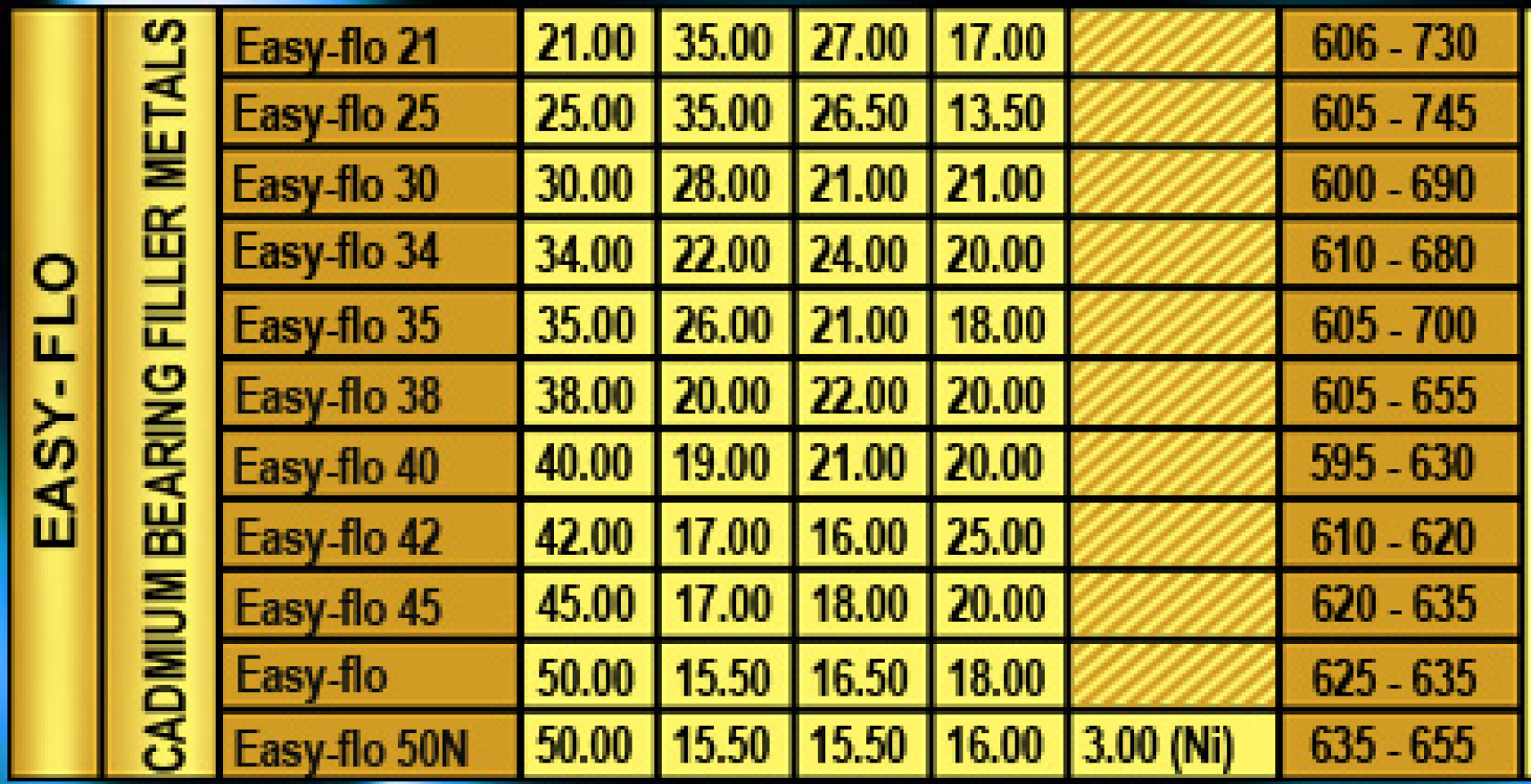
Remarks
Service Temperature :
The silver brazing alloys on this page normally be used for service temperatures between -200C up to _150C without additional instruction.
Parent Metals :
All of these alloys can be used for brazing any steels, copper and copper-based alloys, as well as nickel and nickel-based alloys. However, because of their zinc and cadmium content, there alloys should not be used to braze stainless steels if the finished joints will be exposed to water in service. In this case, early failure of the joint by the mechanism of service corrosion is probable.
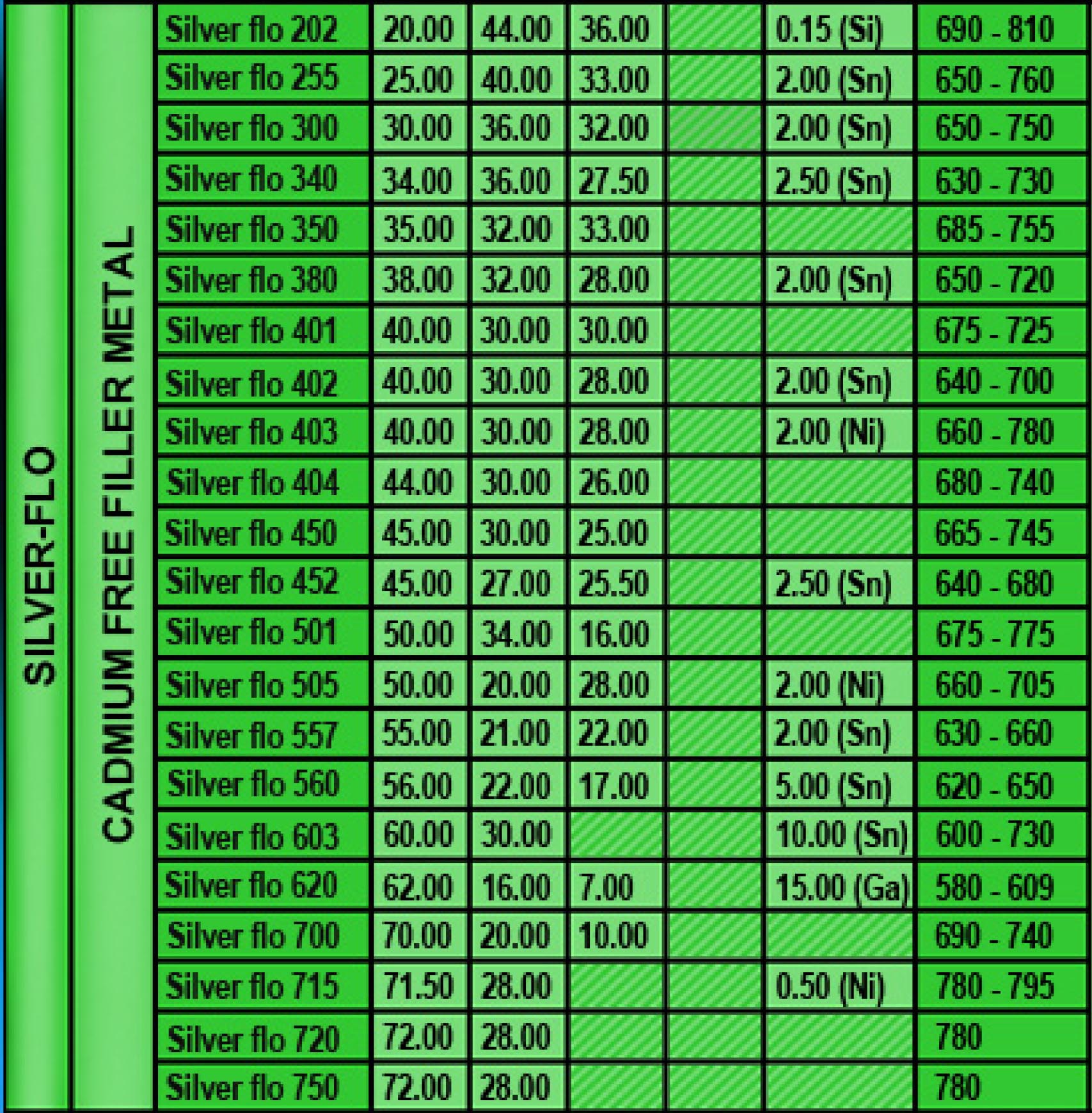
Remarks
Service Temperature :
The silver brazing alloys on this group can generally be used for service temperatures between -200C up to +200C without additional instructions.
Parent Metals :
All can be used for brazing any steels, copper and copper-based alloys as well as for nickel and nickel-based alloys. However, due to their zinc contents, these alloys should not be used to braze stainless steel if the finished joint will be exposed to water in service. In this case, early failure of the joint by the mechanism of service corrosion is probable.
These filler metals can be used :
- For steam turbine blading and heavily galvansed or tinned steel, aluminium brazz tubing.
- For 300 series stainless stell food handling equipment with close joint clearances.
- For food handling equioment requiring a low melting, cadmium-free alloy.
- For silverware, when subsequent joints are made with Braze650
- Filter metals and high conductivity, suitable for both ferrous and non-ferrous alloys.
- For non-ferrous electronic components requiring highest electrical and thermal vacuum conductivity.

Remarks
Service Temperature :
The brazing alloys can be used for service temperature between -55C up to +150C.
Parent Metals :
The phosporous-containing brazing alloys on this page have been developed specially for joining copper-to-copper or copper-based materials to one another, Due to their phosphorous content, it is possible to eliminate the use of a flux when brazing copper-to-copper. The brazing alloys must not be used if the service environment contains sulphur.

Remarks
Service Temperature :
The silver brazing alloys on this page normally be used for service temperatures between -200C up to _150C without additional instruction.
Parent Metals :
All of these alloys can be used for brazing any steels, copper and copper-based alloys, as well as nickel and nickel-based alloys. However, because of their zinc and cadmium content, there alloys should not be used to braze stainless steels if the finished joints will be exposed to water in service. In this case, early failure of the joint by the mechanism of service corrosion is probable.

Remarks
Service Temperature :
The silver brazing alloys on this group can generally be used for service temperatures between -200C up to +200C without additional instructions.
Parent Metals :
All can be used for brazing any steels, copper and copper-based alloys as well as for nickel and nickel-based alloys. However, due to their zinc contents, these alloys should not be used to braze stainless steel if the finished joint will be exposed to water in service. In this case, early failure of the joint by the mechanism of service corrosion is probable.
These filler metals can be used :
- For steam turbine blading and heavily galvansed or tinned steel, aluminium brazz tubing.
- For 300 series stainless stell food handling equipment with close joint clearances.
- For food handling equioment requiring a low melting, cadmium-free alloy.
- For silverware, when subsequent joints are made with Braze650
- Filter metals and high conductivity, suitable for both ferrous and non-ferrous alloys.
- For non-ferrous electronic components requiring highest electrical and thermal vacuum conductivity.